Cyber Safety News Roundup: January 12, 2023

The year 2022 witnessed many notable data breaches due to malware, costing enterprises an average of $4.5 million. 83% of organizations experienced more than one data breach. In 2023, analysts forecast escalating costs associated with cyberattacks. These are attributable to a variety of reasons, including:
- The use of artificial intelligence (AI) tools such as ChatGPT, can be used to automate phishing campaigns (Keary, Tim, 2022).
- Geopolitical instability.
- The looming recession.
In addition, businesses remain as vulnerable as ever. 59% of organizations have not deployed a zero-trust architecture and other critical infrastructure measures (IBM Security, 2022). As a result, cyberattacks may cost the world $10.5 trillion by 2025 (Spitzner, Lance, 2022).
And, cybersecurity events have already surfaced even though 2023 is barely under way. They include:
Play ransomware group bypass ProxyNotShell mitigations
The recent ransomware attack targeting managed cloud hosting services company Rackspace Technology was caused by a zero-day exploit connected to a privilege escalation flaw in Microsoft Exchange Server (referred to as OWASSRF), which combines two Exchange Server flaws -- CVE-2022-41080 and a ProxyNotShell flaw, CVE-2022-41082 (Higgins, Kelly, 2023).
WordPress sites under attack from new Linux malware Exploiting Over 30 CMS Flaws
WordPress sites are being targeted by a newly identified Trojan backdoor program that exploits some 30 vulnerabilities in WordPress plug-ins and themes to inject harmful JavaScript code and redirect users. As a result, more than 15,000 WordPress sites have been breached (Dark Reading, 2023)
BitRAT malware campaign is now using stolen sensitive bank data for phishing
Attackers have compromised a Colombian financial institution and have been using the stolen information of bank customers as lures in phishing emails aimed at spreading the BitRAT malware. A total of 418,777 records with sensitive data of bank customers have leaked. The data includes names, phone numbers, email addresses, addresses, Colombian national IDs, payment records, salary, home addresses, and other data (Montalbano, Elizabeth, 2023).
How to investigate such attacks?
Businesses will be subject to cyber threats for the foreseeable future. But these cyber events should serve as a wake-up call to organizations that constant vigilance is needed to get things back on track. Cybersecurity is not just about managing risk. It is also a strategic issue that shapes organizational effectiveness. Organizations need to be more than cyber-insured or cyber-secured because cyber threats in 2023 will continue to grow and impact our everyday life directly.
This means taking a number of actions. For instance, organizations can examine alerts on their corporate computers using AV/EDR and review each spam/malicious campaign at the organizational level. Doing so will determine if emails are successfully delivered and accessed by users. Business also needs to scan and identify the services/processes running on the infected computers, among many other actions. We also recommend working with a partner who knows the terrain.
How Centific Can Help
At Centific, we define a comprehensive cyber strategy to reduce risk in the digitization effort of our clients and help establish a secure enterprise. Our digital safety framework mitigates various security events, preparing enterprises to become more vigilant against vulnerabilities.
The framework includes:
- The instrumentation and orchestration of overlapping security systems. The overlapping security systems include endpoint monitoring tools, next-generation firewalls, and intrusion prevention systems.
- Breach and attack simulations (BAS) of security policies. AS tools implement Mitre ATT&CK tactics for chaining techniques used by red teams to model adversary behavior.
- DevSecOps. We employ DevSecOps by standardizing processes for security automation while reducing vulnerabilities in deployments of containers and microservices including centralizing user identity and access controls and integrating security scanners in the CI/CD pipeline.
- Intelligent spam filtering. Intelligent spam filtering infuses AI technologies with human centricity to quickly detect, classify, and mitigate activities related to phishing, malware, and other fraudulent forms.
- Data lake security. Our expertise in data lake security ensures governance across the data lifecycle with consistent security standards; access controls for authorization; and encryption. All of this prevents data leakage and cyberattacks, while implementing the appropriate logical structure of the data pipeline. Thus, we ensure risk mitigation of data acquisition, process, enrichment, analytics, and governance.
- Zero-trust security. We’ve de-risked enterprises with the establishment of the zero-trust architecture. Requests are authenticated, authorized, and encrypted prior to access. We’ve established optimized security policies and securitization of identities in order to protect users, assets, and accounts.
- Additional security best practices.
Our Digital Safety Framework includes best practices such as:
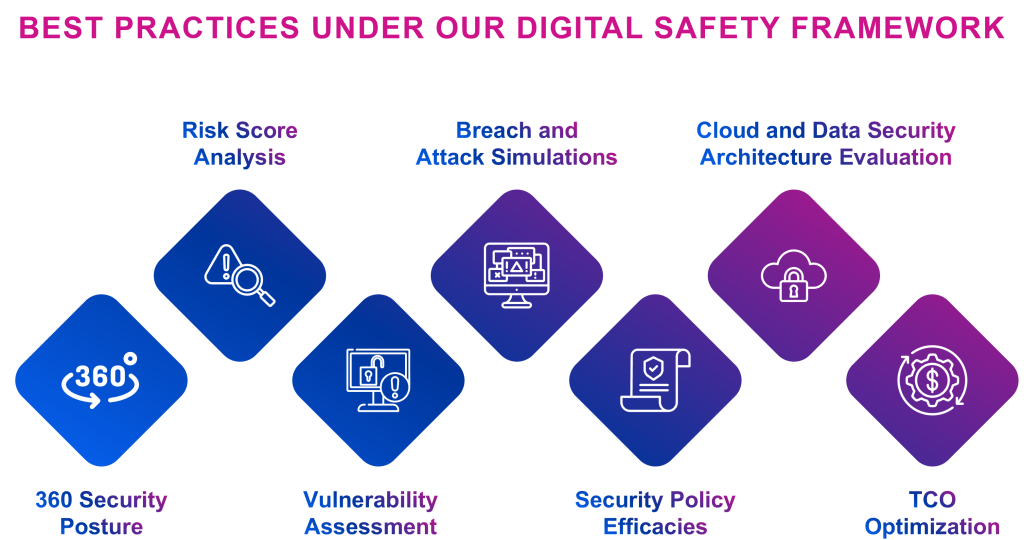
We perform an automated security posture analysis, which then provides a risk score. Based on that, we perform a vulnerability assessment, which helps us plan for security breaches and attack simulations; test security policies; and provide a security architecture recommendation that leads to an optimized total cost of ownership.
Contact us for more information.
Learn more about the authors by visiting their LinkedIn profiles:
- Sanjay Bhakta, VP global head of solutions
- Nitanshu Upadhyay, business solutions consultant
References
- IBM Security, 2022; “Cost of a Data Breach Report 2022”; IBM; Cost of a data breach 2022 | IBM
- Keary, Tim, 2022; “How ChatGPT can turn anyone into a ransomware and malware threat actor”; VentureBeat; How ChatGPT can turn anyone into a ransomware and malware threat actor | VentureBeat
- Spitzner, Lance, 2022; “4 cybersecurity predictions for 2023 — SANS analysts look ahead”; VentureBeat; 4 cybersecurity predictions for 2023 --- SANS analysts look ahead | VentureBeat
- James, Nivedita, 2022; “Cyber Crime Statistics 2023: Cost, Industries, and Trends”; astra; Cyber Crime Statistics 2023 | astra
- Higgins, Kelly, 2023; “Rackspace: Ransomware Attack Bypassed ProxyNotShell Mitigations”; Dark Reading; Rackspace: Ransomware Attack Bypassed ProxyNotShell Mitigations | Dark Reading
- Dark Reading, 2023; “WordPress Sites Under Attack from Newly Found Linux Trojan”; Dark Reading; WordPress Sites Under Attack From Newly Found Linux Trojan | Dark Reading
- Montalbano, Elizabeth, 2023; “BitRat Malware Gnaws at Victims with Bank Heist Data”; Dark Reading; BitRat Malware Gnaws at Victims With Bank Heist Data | Dark Reading
