3 Examples of How GenAI Can Be Hacked to Hurt Businesses

OpenAI recently announced that it had uncovered multiple bad actors associated with nation-states. OpenAI said that the bad actors intended to abuse the company’s generative AI (GenAI) tools to harm others. With the help of Microsoft Threat Intelligence, OpenAI stopped the bad actors and banned them from using the company’s large learning models (LLMs), namely ChatGPT, to cause further harm.
But the incident underscores a startling reality: bad actors are increasingly trying to compromise GenAI applications. Unfortunately, the threat to GenAI from bad actors of all types (state-sponsored and beyond) will only grow as multiple industries adopt GenAI and bad actors gain access to improved GenAI tools that make it easier for them to commit cyberattacks.
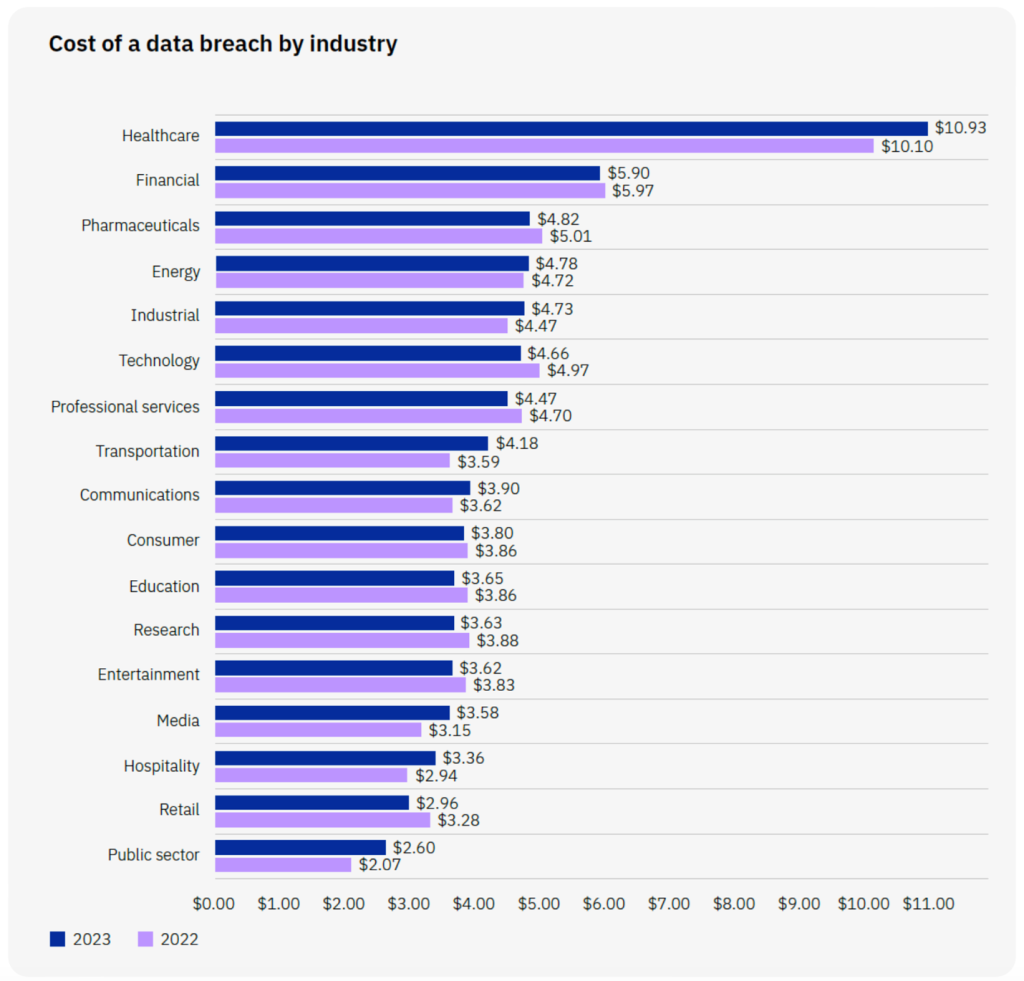
The Cost of a Data Breach
To give decision makers a deeper understanding of how bad actors can compromise GenAI models, it’s important to highlight a few of the most relevant use cases. As more businesses turn to GenAI solutions to meet pressing business needs, they need to be aware of the risks. The cost of a cybersecurity breach can be immense:
How Businesses Are Using GenAI
Businesses ranging from healthcare to retail are applying GenAI in many exciting ways.
Healthcare systems are using GenAI solutions to free up caregivers to focus less on administrative work that takes time away from patient care. For example, as part of a pilot program, emergency room physicians at four HCA Healthcare hospitals have begun using GenAI to draft medical notes from conversations during patient visits.
Retailers are using GenAI in to improve the shopping experience as well. Walmart, for example, recently rolled out a GenAI-powered search capability to simplify online shopping through Walmart’s app and website. Amazon is also raising the stakes for site search by experimenting with a GenAI-powered chatbot, Rufus, which provides shopping assistance while you browse the Amazon site.
And these are only the early adopters. With new developments happening seemingly every second, the list of use cases is constantly growing. But, with any technological growth comes heightened risks.
How Bad Actors Can Harm GenAI
Bad actors have a variety of tools at their disposal to convert your advanced GenAI solutions into potential sources of data breaches. Let's take a look at a three hypothetical, industry-specific scenarios.
1. Healthcare
- The value: LLMs streamline the management of workflows, from patient record keeping to handoffs, improving patient outcomes and nurse experiences.
- The risk: Adding patient data, which is highly coveted by bad actors, to a networked system increases the total attack surface for ransomware.
- The scenario: A hospital relies on a GenAI platform for physicians and nurses to automate recording of clinical notes during patient intake. The hospital integrates the clinical notes for new patients with electronic health records in a centralized data repository and administrative systems like billing. Unfortunately, the centralized data repository becomes compromised, and the GenAI application is breached. Now, the hospital may be liable for the GenAI platform getting compromised, which can result in the centralized data repository and billing functions becoming corrupted.
2. Retail
- The value: GenAI provides customer assistance through chatbots, increasing overall shopper satisfaction and brand loyalty.
- The risk: Bad actors can deploy prompt-hacking tactics to corrupt the chatbot, leading to unfortunate outcomes.
- The scenario: A major retailer deploys a GenAI chatbot to help customers with their shopping needs. The chatbot provides product recommendations, answers questions, and even assists with placing orders. To do its job, it needs to be connected to the retailer’s many internal systems. For example, the chatbot links to the retailer’s inventory to provide real-time stock availability and order management to follow through on customer orders. Unfortunately, bad actors have fed the chatbot malicious data. This data poisoning has manipulated and degraded the chatbot’s responses, embarrassing the business. The breach has also spread throughout the company’s inventory, order management, and customer data platform.
3. Financial Services
- The value: GenAI helps retail banks assess loan risks by processing information and providing data-driven recommendations faster than humanly possible.
- The risk: Collecting sensitive customer data to enable the GenAI application increases the risk of loss in the event of a hack.
- The scenario: A retail bank’s loan origination department relies on GenAI to assess loan risks. To do this, the GenAI-powered loan risk tool integrates with internal and external databases, to retrieve an applicant’s credit reports and scores from credit bureaus and to review the applicant’s banking history. Unfortunately, bad actors exploit an ordinary security weakness, gaining access to this treasure trove of sensitive data scattered throughout the bank’s systems. Now, the bank runs the risk of additional financial and reputational loss from fines and reduced client trust.
How Bad Actors Can Corrupt LLMs
To corrupt GenAI applications, bad actors often can rely on one of several techniques, each of which is rapidly evolving. The following are only a few examples of LLM-based security issues identified
OWASP top 10.
Data Poisoning
- How it works: Bad actors manipulate the training data that drives the LLM. By subtly introducing biased, misleading, or incorrect information, they can skew the model’s output, leading to harmful or discriminatory responses.
- Example: Feeding an LLM a dataset containing bigoted language can lead the model to produce text that reflects those biases.
Model Inversion Attacks
- How it works: Adversaries send carefully crafted prompts to the LLM designed to extract sensitive information that may have been part of the model’s training data.
- Example: Attackers could try to retrieve private information like medical records or financial data from the model’s training data set.
Adversarial Examples
- How it works: Bad actors subtly tweak text inputs in ways that are imperceptible to humans but cause the LLM to misclassify or misinterpret content.
- Example: Changing a few words or punctuation in a sentence could cause the model to misunderstand the sentiment of a piece of text or trigger it to generate unsafe content.
Prompt Engineering and Jailbreaking
- How it works: Attackers meticulously craft prompts to get around the LLM’s safety mechanisms or trick the model into revealing sensitive information. This can involve using manipulative language or exploiting loopholes in the model’s logic.
- Example: A hacker might coax a usually harmless LLM into generating code that could be used for malicious purposes.
Model Extraction
- How it works: Adversaries replicate the functionality of an LLM by repeatedly querying it and analyzing its responses. They aim to create a smaller, less powerful, but potentially less secure copy of the model.
- Example: Using a large volume of queries, a bad actor might attempt to partially reconstruct a proprietary LLM.
How Business Can Fight Back: A 360-Degree Approach
Although this might sound like doomsaying, there’s good news too. You can take steps to protect your business. We at Centific recommend that you adopt a 360-degree approach to GenAI cybersecurity, incorporating data loss prevention (DLP) and other important frameworks.
For example, At Centific, we help CISOs, heads of fraud, and heads of risk and compliance test their GenAI models using frameworks like MITRE ATLAS and tools like Caldera or Counterfeit to test GenAI models for vulnerabilities.
The MITRE ATLAS Framework helps organizations prioritize defensive measures, test security controls against real-world threats, and improve threat-hunting capabilities. To appreciate just how thorough the MITRE ATLAS Framework is, explore the MITRE ATLAS Matrix, which maps common steps that bad actors take to poison GenAI models.
Of course, using the right frameworks and tools is only a small part of a comprehensive, 360-degree approach to GenAI cybersecurity. Centific is here to help you protect yourself and your business while you maximize the benefits of GenAI.
Learn more about our digital safety services on our website.
