

Topics
4 min read time
Multilingual instruction tuning and safety alignment require high-quality, diverse training data. But collecting that data, especially for low-resource languages and sensitive topics like privacy or misuse, remains slow, expensive, and inconsistent.
In our VLDB 2025 paper, we have introduced AI-assisted annotation, a scalable human-in-the-loop framework that combines prompt writers, quality assurance based on large language models (LLMs), and synthetic personally identifiable information (PII) tools to accelerate multilingual prompt generation. By using LLMs not just as generators, but as judges, we have reduced annotation time by over 40% without sacrificing coverage, quality, or instruction compliance.
We deployed AI-assisted annotation to create more than 40,000 high-quality prompts across 13 languages, covering tasks like personal data redaction, safety alignment, and misuse detection. Those are all critical areas for LLM safety evaluation.
The challenge: scaling prompt writing for low-resource locales
Instruction tuning and safety alignment depend on training data that reflects realistic, nuanced user inputs. For high-stakes applications like identifying harmful intent or protecting personal data, researchers often rely on human-written prompts to capture edge cases and ambiguity. But this manual work doesn’t scale, especially when:
Prompts must be written in underrepresented languages
They must include synthetic but realistic PII
They must follow complex, high-precision instructions
And they must avoid repetition while maintaining natural variation
Manual workflows struggle to meet all these constraints at scale, making it difficult to build multilingual safety datasets that are both broad and reliable.
The framework: AI-augmented prompt generation with LLM-as-a-judge
AI-assisted annotation introduces a modular, AI-supported pipeline to improve throughput, quality, and diversity in human-authored prompts. The system includes:
Synthetic PII Suggestion: we recommend structured, locale-specific PII—like Aadhaar numbers or health IDs— using a tool that draws from curated templates and fake data generators.
LLM-as-a-judge for instruction following: instead of using LLMs to write prompts, we use them to evaluate and score human-written ones. Judges assess instruction of compliance (e.g., word count, structure, content type) and provide instant feedback to writers.
Similarity checking: We apply vector-based checks to flag lexically or semantically repetitive prompts, enforcing diversity across submissions.
Maintaining Data Diversity: As LLM training would require good coverage and diversity of input data, authors are provided with structured guidance on domain, PII type combinations, text length.
Unlike traditional pipelines, AI-assisted annotation delivers immediate feedback loops, reducing rework and improving consistency across annotators and languages.
Deployment at scale: 13 languages, 40,000+ prompts
We deployed AI-assisted annotation with Centific’s professional annotation teams to generate multilingual prompts across 13 locales: Arabic (UAE), Finnish (Finland), Hindi (India), Norwegian (Norway), Dutch (Belgium), Dutch (Netherlands), Polish (Poland), Portuguese (Brazil), Portuguese (Portugal), Swedish (Sweden), Vietnamese (Vietnam), and Chinese (China), Chinese (Singapore).
Each prompt was written by a human, guided by tools and judged by an LLM for accuracy and coverage. Prompts were designed to simulate:
Domain (e.g., IT, CPG, Healthcare, Finance)
Requests containing region-specific PII (e.g., local ID numbers, bank account formats)
Malicious or ambiguous intent (e.g., phishing, scams)
Natural language diversity (e.g., tone, phrasing, cultural context)
Task category (summarization, rewrite, translation, chain-of-thought)
Tasks included redaction, classification, and detection of misuse, aligned with the needs of LLM safety benchmarks.
Results: 40% faster, with no drop in quality
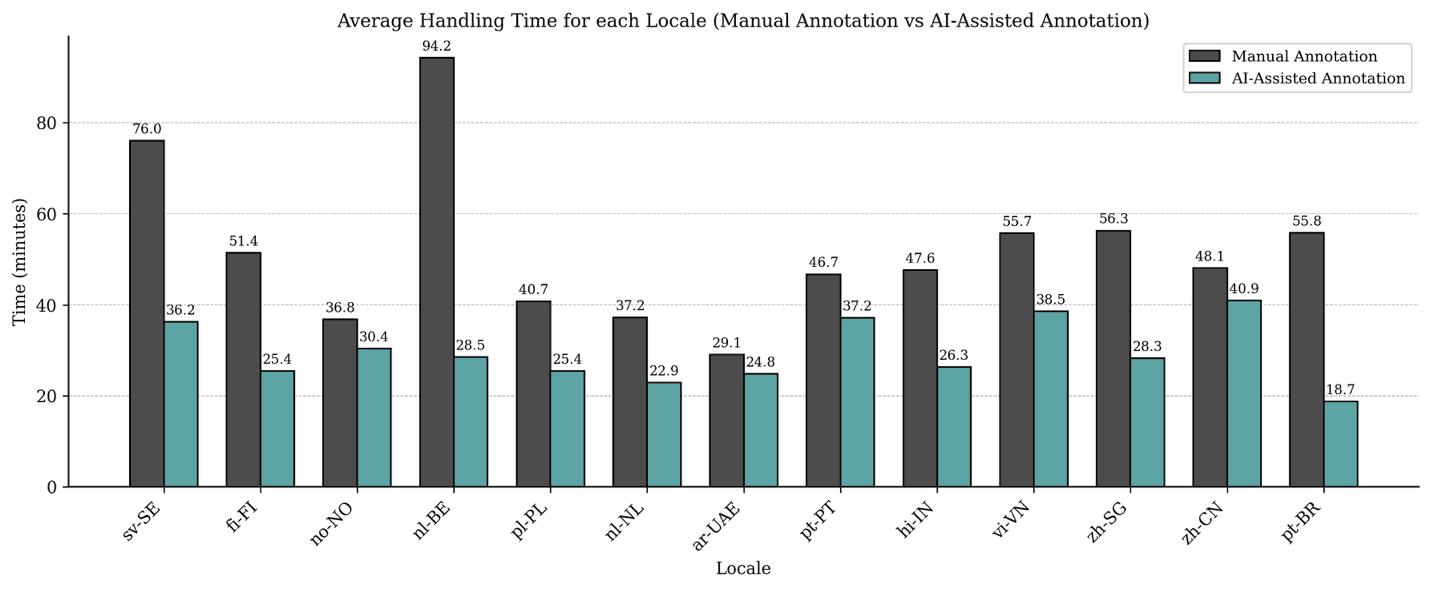
We ran a comparative study of AI-assisted annotation against a traditional human-only workflow. Key results:
40% reduction in average handling time per prompt, driven by fewer revision cycles and better real-time feedback.
Significant gains in instruction compliance, especially word count, PII formatting, and language specificity.
Higher lexical and structural diversity, enforced through AI-based repetition checks.
These gains did not come at the cost of quality: judged correctness, completeness, and naturalness of prompts were statistically equivalent across workflows.
Why it matters
AI-assisted Annotation addresses a known bottleneck in LLM alignment: scalable, high-quality prompt generation in underrepresented languages. The framework:
Improves multilingual coverage for red-teaming, safety tuning, and PII detection
Reduces annotation cost without losing linguistic or structural diversity
Provides a reusable pipeline that supports multilingual model evaluation and instruction tuning
By decoupling prompt generation from manual review, and using LLMs as real-time QA agents, we improve both speed and safety in data creation.
What’s next
We are expanding AI-assisted annotation to support longer tasks, multi-turn dialogue, and complex chain-of-thought reasoning prompts. Future work includes evaluating LLM-as-a-judge alignment with human quality scores and extending the framework to unseen languages and scripts.
Are your ready to get
modular
AI solutions delivered?
Connect data, models, and people — in one enterprise-ready platform.
Latest Insights
Connect with Centific
Updates from the frontier of AI data.
Receive updates on platform improvements, new workflows, evaluation capabilities, data quality enhancements, and best practices for enterprise AI teams.


